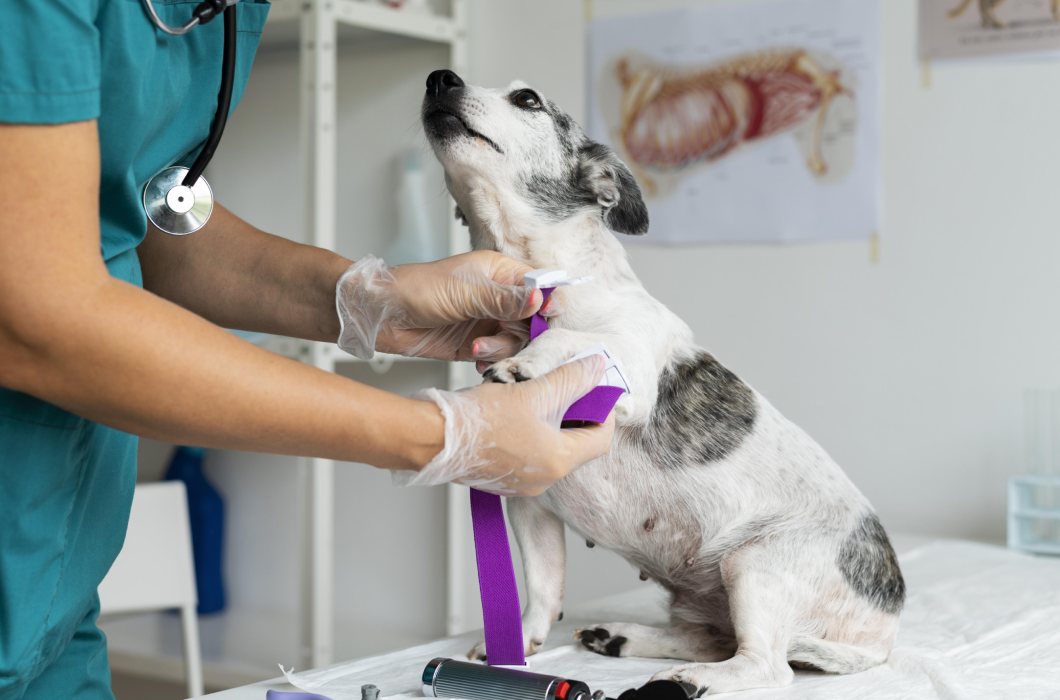
This type of blood test gives a complete picture of the animal’s health status. Today, this is one of the most informative methods of laboratory research. Visual examination and anamnesis cannot give a complete picture, since many pathological processes go unnoticed. In addition, cats often behave restlessly when visiting a doctor; they burst, bite and hiss. In this state, identifying the problem may be difficult, but analysis will show the situation in detail and clearly.
What problems does a biochemical blood test solve?
Biochemical blood tests performed on animals allow:
- Reduce the time required for diagnosis.
- The state of water-salt balance, metabolic disorders and the level of microelements in the blood are assessed.
- Determine the degree of functioning of organ systems.
- Determine a detailed treatment prognosis, monitor and adjust it.
- Prevent the problem or stop it in its early stages.
Stages of biochemical blood testing
Fix a cat or dog
Vein hair removal
Skin disinfection
Wire installation
Blood collection
Making rules:
do not feed for about 8 hours, but no more than 14 hours before taking blood;
stop taking medications or contact a veterinarian
Reduce stress
What can a biochemical blood test determine?
A biochemical study of the blood of cats and dogs is aimed at studying more than two dozen metabolic markers of the body, the deviation of which from the norm is a sign of diseases or disorders of organ systems, as well as the development of metabolism.
Uric acid
Uric acid is found in the blood primarily in the form of salts, urates, and is excreted primarily by the kidneys, thus removing excess nitrogen from the body. In most mammals, uric acid is secreted by nephron cells and is actively absorbed into the renal tubules.
Total protein
Blood plasma proteins are involved in immune, inflammatory reactions and the process of blood coagulation, help maintain acid-base balance, perform regulatory, motor, protective, nutritional and other functions. Some proteins serve as enzymes, antibodies, clotting factors, and transporters. The main site of plasma protein synthesis is the liver. Also, the place of their formation is the immune system.
The concentration of total protein is determined by the content of albumin and globulins in the blood.
Total bilirubin
Total bilirubin is a combination of conjugated (direct) and unconjugated (free, indirect) bilirubin fractions. Free (unconjugated) bilirubin is a calculated indicator and represents the difference between the values of total and direct (conjugated) bilirubin.
ALT
In dogs and cats, the highest concentrations of ALT are found in hepatocytes (especially near the portal area), so serum ALT determinations are routinely included in biochemical studies in these animals. This enzyme is also present, but in lower concentrations, in the kidneys, pancreas, intestines, skeletal and myocardial tissues, and red blood cells. In some mammals (for example, rabbits), the content of ALT in the liver and heart muscle is almost the same.
Albumin
Albumin is synthesized in hepatocytes and provides approximately 75-80% of plasma oncotic pressure. Albumin makes up 30-45% of the total protein. Increased albumin concentration is usually the result of dehydration and hemoconcentration. Hypoalbuminemia may result from leakage of albumin into the glomerular ultrafiltrate and suggests glomerular damage and chronicity of the disease. In liver diseases, hypoalbuminemia is not detected until more than 70% of the function of the liver system is impaired.
GGT
Gamma glutamyl transferase is an enzyme involved in amino acid metabolism.
GGT is found in high concentrations in the kidneys, pancreas, and mammary glands, and in lower concentrations in the liver, spleen, intestines, lungs, and sperm. GGT is not found in skeletal muscle and myocardium. In the kidneys, GGT is localized on the luminal surface of the cells of the proximal renal tubules, and if they are damaged, the enzyme leaks into the urine. Liver pathology is the most common cause of increased GGT activity in the blood serum, which is due to the localization of the enzyme.
Visit the veterinary clinic, follow the veterinarian’s instructions and be healthy.